Top 13 main factors affecting the consumption of centrifugal sand pumps
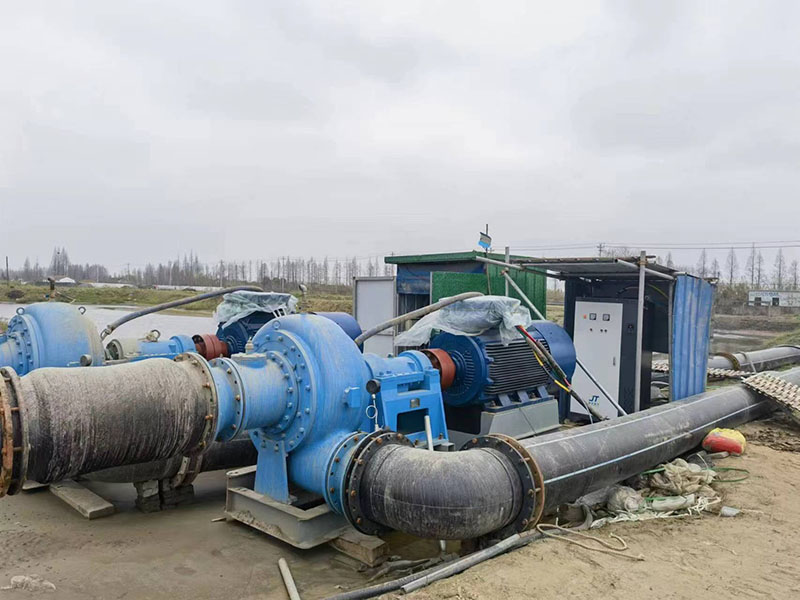

Eventually, users often ask me: "How long can the pump continue to work?" Of course, my answer is "it depends."
As a mechanical product, there are many factors that affect it, but the most common factors are:
1. Radial force of centrifugal sand pump
Many coal mine slurry pump industry statistics indicate that the largest cause of unplanned centrifugal pump downtime is bearing and/or mechanical seal failure. Bearings and Seals They are early indicators of pump health and a precursor to failure within the pumping system. Anyone who has worked in the pump industry for any length of time probably knows that best practice number one is to run your pump at or near the best efficiency point (BEP). At BEP, the pump will be designed to withstand minimal radial forces. When operating away from the BEP, the resultant vector of all radial forces is at a 90¡ã angle to the rotor and attempts to deflect and bend the pump shaft. High radial forces and consequent shaft deflection are a killer of mechanical seals and a factor in shortened bearing life. If the radial force is large enough, it can cause the shaft to deflect or bend. If you stop the pump and measure the run out of the shaft, you will find nothing wrong since this is a dynamic condition, not a static condition. A curved shaft running at 3,600 rpm will deflect twice per revolution, so it will actually bend 7,200 times per minute. This high cycle deflection makes it difficult for the sealing surfaces to maintain contact and maintain the fluid layer (film) required for proper seal operation.
Taian Ocean Pump Co., ltd With dredge pump packing seal, easy operation.and some industrial slurry pump must use mechanical seal ,must be keep in good condition .
2. Lubricating oil contamination
For sand pump ball bearings, more than 85% of bearing failures are caused by contamination, which may be dust and foreign matter, or water. Just 250 parts per million (ppm) of water can shorten bearing life by four times. The service life of lubricants is critical.
We suggest you keep checking lubrication oil for bearing.
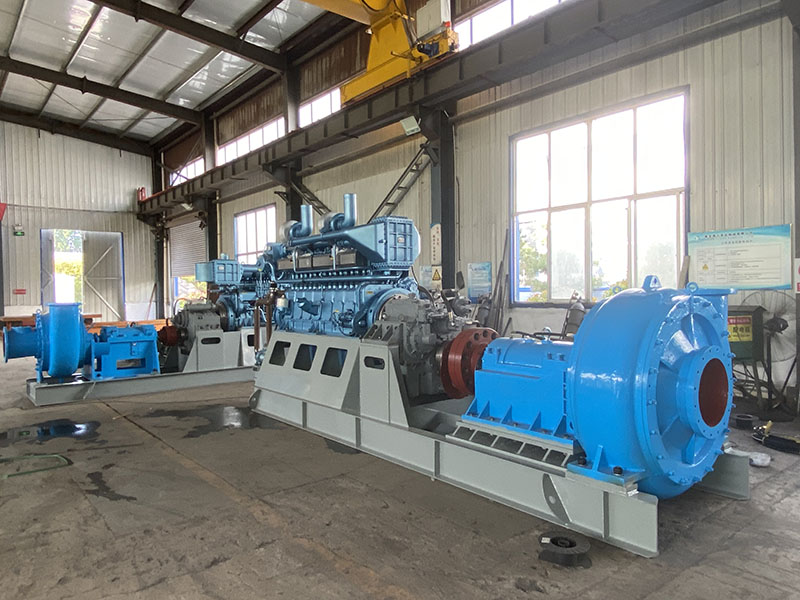

3. Suction pressure of centrifugal sand pump
Other key factors affecting bearing life include suction pressure, driver alignment and, to some extent, pipe strain. For the ANSI B 73.1 single-stage horizontal cantilever process pump, the axial force generated on the rotor is toward the suction inlet, so the reaction suction pressure to a certain extent and within a certain limit will actually reduce the axial force, thereby reducing the thrust bearing load, extending service life. Consider using big pipe to connect with suction size of pump that will also useful,and also need to calculate the flow speed with different material .
4. Power end alignment
Misalignment of the pump and power end can overload the radial bearings. The life of a radial bearing is exponentially related to the degree of misalignment. For example, with a slight deviation (misalignment) of just 0.060 inches, end users may experience bearing or coupling problems after three to five months of operation. But if the deviation is 0.001 inches, the same pump may run for more than 90 months.
5. Dredging pipeline strain
Dredging Pipe strain is caused by misalignment of the suction and/or discharge pipes to the pump flange. Even in robust pump designs, piping strains can easily transfer these potentially high stresses to the bearings and their corresponding bearing housing matings. Forces (strains) can cause a bearing fit to be out of round and/or inconsistent with other bearings, causing the centerline to lie in a different plane.
Taian Ocean Pump Use the HDPE Dredge pipe .HDPE Dredging Pipe with non-toxic, odorless, good heat and cold resistance. The pipe is made by PE100 high density polyethylene materials. HDPE dredge pipes are widely used for dredging industries, dredger pipelines, sand pumping pipelines, etc.
6. Fluid properties
Fluid properties such as pH, viscosity and specific gravity are key factors. If the fluid is acidic or corrosive, the wetted parts of the pump (such as casing and impeller materials) need to hold up (corrosion-resistant) in use. The solids content of the fluid as well as its size, shape and abrasiveness are all factors.
The dredging pump mainly contains sand- and mud-containing media, sharp stones, hard sand, silica sand, and kaolin, which are mainly worn through the impeller, pump shell, and front guard plate.
Taian OCEAN Pump made the dredge pump with high chrome alloy Cr26 With Good Performance for Wear Resistance.
7. Frequency of use (service)
Frequency of use (service) is another important factor: How often is the pump started within a certain period of time? I have personally witnessed pumps starting and stopping every few seconds. Pump wear rates are much higher during these services than when pumps are operated continuously under the same conditions. In this case, the system design needs to change urgently. Under the same conditions, a pump with submerged suction operates more reliably than a pump with suction. A suction-up condition requires more work and creates more opportunities for air inhalation or worse, a dry run.
Suggest like Submersible Dredge Pump ,When working whole pump submerged in water £¬which can not suction air .
But like Horizontal Dredge Pump driven by motor or diesel engine on land or boat need to first pump out all air £¬water or slurry will come in pump £¬which will also make pump dry running .
8. Net positive suction head margin
The difference between the inlet pressure and the lowest pressure level within the pump is called NPSH: Net Positive Suction Head. NPSH represents the pressure loss inside the first part of the pump housing.
The pressure inside the pump changes from the inlet on the suction side to the discharge port on the discharge side. In the first part of the pump, the pressure decreases before increasing above the suction pressure on the discharge side.
The performance of the NPSH pump is shown in the figure to the right. The Y-axis of the NPSH curve after NPSH calculation represents H (head), and the X-axis represents Q (flow rate).

If the inlet pressure is too low, NPSH will cause the minimum pressure in the pump to drop below the evaporation pressure of the pumped liquid. As a result, cavitation occurs within the pump, causing noise and failure.
The greater the margin between the available net positive suction head (NPSHA, or installation NPSH) and the required net positive suction head (NPSHR, or required NPSH), the more likely it is that the pump will cavitate. The smaller it is. Cavitation can cause damage to the pump impeller, and the resulting vibrations can affect seal and bearing life.
9. Centrifugal sand pump speed
The operating speed of the pump is another critical factor. For example, a pump running at 3,550 rpm will wear out 4 to 8 times faster than a pump running at 1,750 rpm. So the lower the pump speed, the slower it will wear. For Dredge Sand Pump Rotation Speed, normally need to choose the suitable flow capacity and pump head and then to check pump speed to match with diesel engine speed with gear box .Try to choose the slowest speed .
10. Centrifugal sand pump impeller balance
An unbalanced impeller on an overhung pump or some vertical designs can cause shaft wobble, a condition that deflects the shaft as a result of radial forces when the pump is operated away from the BEP. Radial deflection and shaft wobble may occur simultaneously. It is recommended that the impeller be balanced in accordance with at least ISO 1940 G 6.3. If the impeller is cut for any reason, it must be re balanced.
11. Dredging pipeline layout and inlet flow rate
Another important consideration for extending pump life is the way the lines are laid out, i.e. how the fluid is "loaded" into the pump. For example, a bend in the vertical face of the pump suction side will have less harmful effects than a horizontal bend - the impeller will be hydraulically loaded more evenly, and therefore the bearings will be loaded more evenly. Additionally, the suction side fluid velocity should be kept below 10 feet/second. It is recommended to keep the velocity below 8 ft/sec, 6 ft/sec is better (assuming non-slurry fluid). Laminar flow instead of turbulent flow affects the way the impeller is loaded and changes the rotor dynamics.

12. Centrifugal pump operating temperature
Whether it is high or low temperature, the operating temperature of the pump, especially the temperature change rate, will have a great impact on the life and reliability of the pump. The operating temperature of the pump is very important and the pump must be designed to accommodate the operating temperature. But more important is the rate of temperature change. It is recommended to keep the rate of change to less than 2 degrees Fahrenheit per minute. Different masses and materials expand and contract at different rates, which affects gaps and stresses.
13. Dredging pump housing penetration
Although not often considered, the reason casing penetrations are an option for ANSI pumps rather than the standard is that the number of pump casing penetrations will have an impact on the life of the pump because these locations are susceptible to corrosion and stress gradients (l high) prime position. Many end users wish to drill and tap the housing for drain, vent, instrumentation ports. Every time you drill and tap a casing, you leave a stress gradient in the material that becomes a source of stress cracks and a place for corrosion to begin.
-
WhatsApp
-
E-MailE-Mail:oc@tsbeng.com
-
WeChatWeChat:yychen19







